Overview
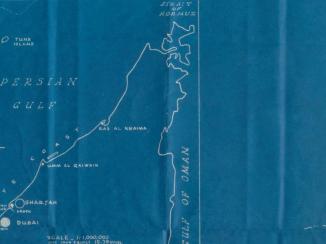
Qatar is an Arab emirate situated on a peninsula on the southern coast of the Gulf, with a population of approximately two million persons. Its capital, Doha, is located on the country’s eastern coast.
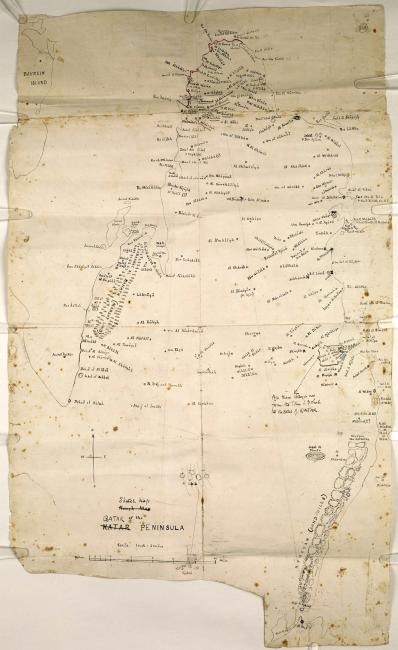
Doha emerged in the late nineteenth century from the earlier town of Al Bidda. Prior to the emergence of Al Bidda, the town of Zubarah 18th-century town located 105 km from Doha. was the peninsula’s most important settlement. Situated on the peninsula’s northwest coast, facing Bahrain, Zubarah 18th-century town located 105 km from Doha. was one of the most important trading posts in the Gulf during the eighteenth century.

Right up until the mid-nineteenth century, European travellers and mapmakers generally regarded Qatar as being part of Bahrain. The British Government first recognised Qatar’s autonomy from Bahrain in 1868, when the British Political Resident A senior ranking political representative (equivalent to a Consul General) from the diplomatic corps of the Government of India or one of its subordinate provincial governments, in charge of a Political Residency. , Lewis Pelly, signed an agreement with Shaikh Jassim bin Mohammad al-Thani.
In the years that followed, Qatar wavered between an acceptance of British and Turkish-Ottoman rule; a Turkish garrison was maintained in Doha between 1871 and 1913. In 1916, in the wake of the demise of the Ottoman Empire, Britain signed a formal treaty with Qatar, establishing the emirate as a British protectorate. However, Britain did not appoint a Political Officer in Qatar until 1949, the emirate’s affairs being overseen until then by the Political Agent A mid-ranking political representative (equivalent to a Consul) from the diplomatic corps of the Government of India or one of its subordinate provincial governments, in charge of a Political Agency. in Bahrain.
Oil was discovered in Qatar in 1939, after Shaikh Abdullah bin Jassim al-Thani had signed an oil exploration concession with the Anglo-Persian Oil Company in 1935. Prior to the large-scale exploitation of the country’s oil and natural gas reserves in the 1950s, Qatar’s inhabitants were almost entirely dependent on the Gulf’s pearl fisheries for their livelihood.
Qatar was granted independence from Britain on 3 September 1971.
KEY MOMENTS FROM BAHRAIN’S HISTORY IN THE INDIA OFFICE RECORDS INCLUDE
- 1782: The earliest recorded mention of Zubarah 18th-century town located 105 km from Doha. in the India Office The department of the British Government to which the Government of India reported between 1858 and 1947. The successor to the Court of Directors. Records (IOR/R/15/1/3, f.95)
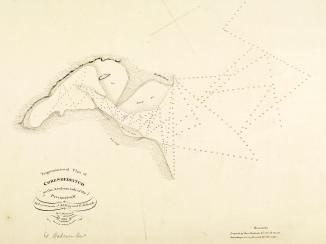
- 1823: The first survey of Qatar’s coastline (IOR/X/3694)
- 1868: Agreement between Qatar and the British (Mss Eur F126/38, ff.124v -126)
- 1913: The Death of Shaikh Jassim (IOR/R/15/2/26, f.155)
- 1935: The Qatar Oil Concession (IOR/R/15/2/416, ff.13-22)
- 1939: The discovery of oil in Qatar (IOR/R/15/2/418, f.214)